During the past few years, U.S. manufacturers have massively increased their investment in robots. According to the Association for Advancing Automation, for example, North American manufacturers spent $1.249 billion to purchase 23,903 robots in the first half of 2022. The dollar amount is 29 percent more than sales for the first half of 2021.
Similarly, according to ASSEMBLY’s annual Capital Equipment Spending Survey, sales of six-axis robots, SCARAs, grippers and other robotic technology are forecast to increase 20 percent, from $600 million in 2022 to $720 million in 2023. Some 37 percent of U.S. assembly plants will purchase robots next year, which ties the record high set in 2022.
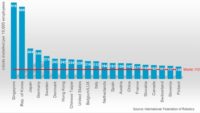
Despite those rosy numbers, however, U.S. manufacturers are lagging in terms of robot deployment. China’s massive investment in industrial robotics has put the country near the top ranking of robot density, surpassing the United States for the first time. Among Chinese manufacturers, the number of operational industrial robots relative to the number of workers hit 322 units per 10,000 employees in 2021, according to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR). China now ranks fifth in the world in robot density. The top four are South Korea, Singapore, Japan and Germany. The U.S. is 9th.
“Robot density is a key indicator of automation adoption in the manufacturing industry around the world,” says Marina Bill, IFR president and group vice president for robotics and discrete automation at ABB Inc. “The new average of global robot density in the manufacturing industry surged to 141 robots per 10,000 employees—more than double the number six years ago. China’s rapid growth shows the power of its investment so far, but it still has much opportunity to automate.”
Driven by the high volume of robot installations in recent years, Asia’s average robot density surged by 18 percent annually since 2016 to 156 units per 10,000 employees in 2021. The European robot density had been growing by 8 percent per year in the same period of time reaching 129 units. In the Americas, it was 117 robots, an annual growth rate of 8 percent.
Korea hit an all-time high of 1,000 industrial robots per 10,000 employees in 2021. This is more than three times the number reached in China and makes the country No. 1 worldwide. Singapore takes second place with a rate of 670 robots per 10,000 employees in 2021. Singapore’s robot density had been growing by 24 percent on average each year since 2016.