Home » electric car manufacturing
Articles Tagged with ''electric car manufacturing''
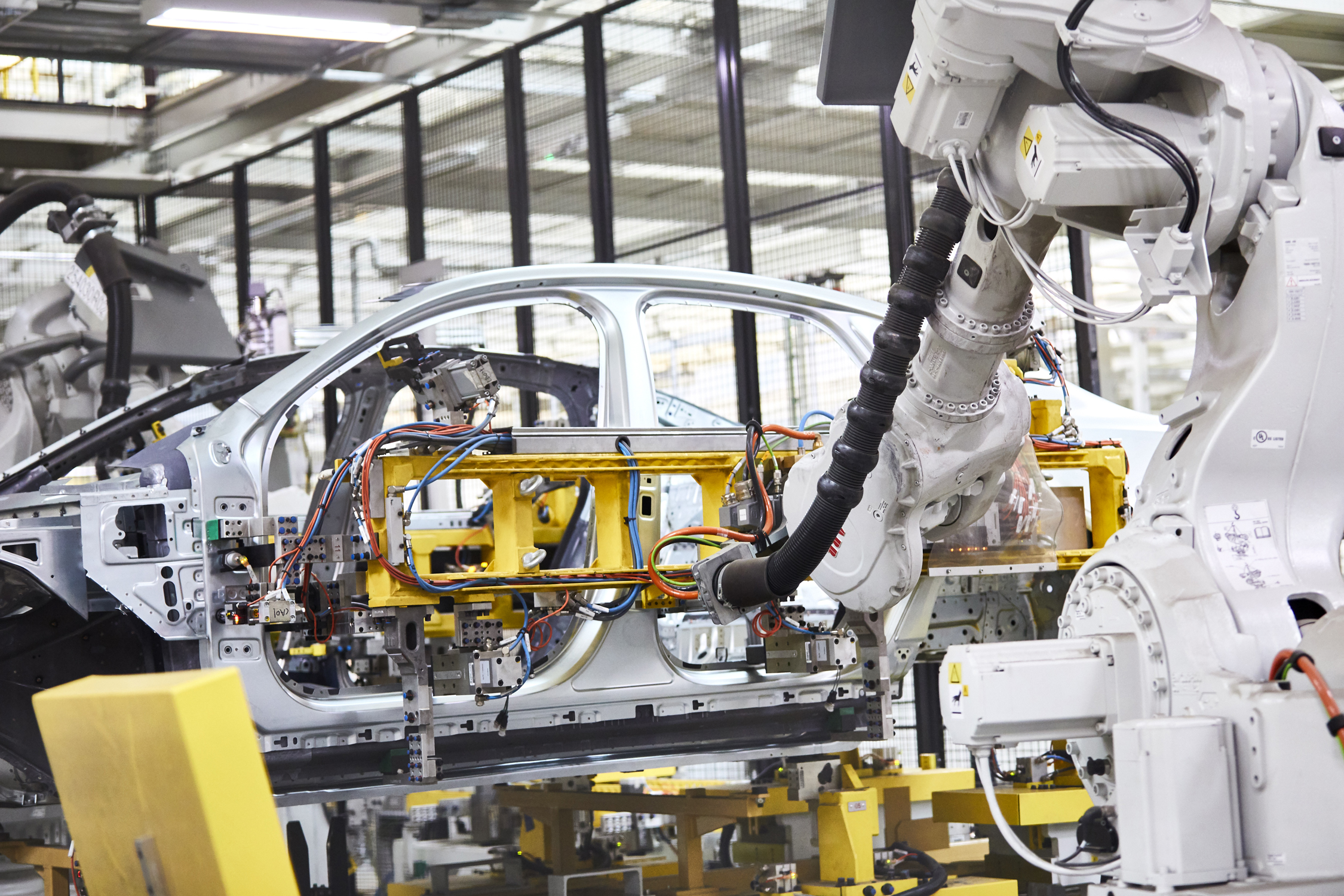
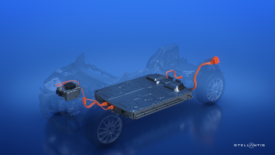
Tesla Rethinks the Assembly Line
The “unboxed” production concept could slash EV manufacturing costs and reduce factory space.
May 8, 2023
Get our new eMagazine delivered to your inbox every month.
Stay in the know on the latest assembly trends.
SUBSCRIBE TODAY!Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing