Home » Keywords: » epoxy adhesives
Items Tagged with 'epoxy adhesives'
ARTICLES
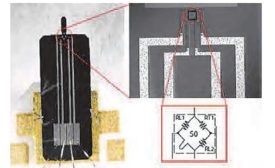
Automated Dispensing for EV Motor Assembly
A fully automated line dispenses and cures a filled, two-part epoxy to encapsulate bus bars for ev motors.
June 8, 2023
Assembling EV Motors With Adhesive
Magnets, rotors, shafts, stators and other metal components require epoxy.
May 17, 2022
Carbonic Cleaning for Adhesive Bonding
Carbonic cleaning safely and consistently removes contaminants from materials to prepare them for adhesive bonding
May 1, 2020
Bubble-Free Potting of Capacitors
Scheugenpflug’s vacuum potting system ensures quality encapsulation of high-voltage capacitors for medical devices.
May 1, 2018
Alternative UV-Curing Adhesives
A new generation of UV-curing silicones and epoxies are increasingly being used in automotive and electronics applications.
March 6, 2018
Adhesives Aid Truck and Trailer Assembly
High-strength adhesives and sealants can improve the durability and appearance of trailers and truck bodies, while enhancing throughput.
June 7, 2017
Heat-Resistant Adhesives
Epoxies top the list of adhesive chemistries that can take the heat.
May 5, 2017
Never miss the latest news and trends driving the manufacturing industry
Stay in the know on the latest assembly trends.
JOIN TODAY!Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing